Neural Information Processing
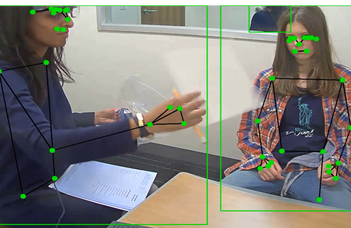
Description of Activities
The core activities at the Neural Information Processing Group (NIPG) are related to artificial intelligence including GOFAI and deep learning with focusing on their combination (called Composite AI) and on applications for human-machine interactions. We consider deep learning as “sensors” and GOFAI as higher order knowledge that we learn in school. This is necessary for our applications where we combine image and video processing, speech, textual information, and physics among other things.
The Department has been supported by Robert Bosch Ltd., and this support is due to the results of NIPG. We are part of the National AI Laboratory, we have an industrial R+D+I project called MOBOT for the development of the visual system of a robot having the task of a regular warehouse inventory, we are involved in several “micro-projects” of the large HumanE-AI EU project, and we are to take part in a project of EIT Digital on fire detection. Similar projects have been finished successfully in the past, including EU projects, projects from the US Air Force, Honda Europe and Panasonic PINTL and OWL, for example.
Research Interests
- Human-machine interaction
- Applications in diagnostics, treatments, and training, both behavioral and physical
- Detecting and evaluating human-human interactions
- Information fusion, including image-video, speech, and text
- Temporal processes and prediction
Research/service concepts/Methodology
- Computers, GPUs,
- Software tools, either our own developments, or tools from the Internet with appropriate licenses
- Deep learning
- Combining deep learning with Good old-fashioned AI (GOFAI), called Composite AI
Research Staff
- 3 senior researchers
- 1 programmer
- 10 PhD students at different levels
Projects
https://nipg.inf.elte.hu/#grants-page
5 important publications in the field
- Kopácsi, L., Baffy, B., Baranyi, G., Skaf, J., Sörös, G., Szeier, S., Lőrincz, A. and Sonntag, D. (2023) ‘Cross-Viewpoint Semantic Mapping: Integrating Human and Robot Perspectives for Improved 3D Semantic Reconstruction’, Sensors, 23(11), pp. 5126:1–5126:17.
- Baranyi, G., Dos Santos Melício, B. C., Gaál, Z., Hajder, L., Simonyi, A., Sindely, D., Skaf, J. Dušek, O., Nekvinda, T. and Lőrincz, A. (2022) ‘AI Technologies for Machine Supervision and Help in a Rehabilitation Scenario’, Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 6(7), pp. 48:1–48:25.
- Fóthi, Á., Soorya, L. and Lőrincz, A. (2020) ‘The Autism Palette: Combinations of Impairments Explain the Heterogeneity in ASD’, Frontiers in Psychiatry, 11, pp. 503462:1–503462:23.
- Varga, V. and Lőrincz, A. (2020) ‘Reducing human efforts in video segmentation annotation with reinforcement learning’, Neurocomputing, 405, pp. 247–258.
- Véges, M., Varga, V. and Lőrincz, A. (2019) ‘3D human pose estimation with siamese equivariant embedding’, Neurocomputing, 339, pp. 194–201.


